You are in the planning stage of the network configuration for your Database Machine. The requirements are:
1. A fault-tolerant network, providing higher availability for connections to database instances
2. Fault tolerance providing higher availability for connections to perform management functions on the database and storage servers.
3. Full monitoring of all Database Machine components using Enterprise Manager
Which three components require external Ethernet network cables to connect your existing network infrastructure to your database machine to satisfy this requirement?
- A. Database servers
- B. Exadata storage servers
- C. InfiniBand storage servers.
- D. Power distribution units (PDUs)
- E. Cisco Ethernet switch
Answer : A,D,E
You are using Hybrid Columnar Compression for a table stored in a tablespace that is contained in an Exadata-based ASM diskgroup. Identify three statements that correctly explain where the compression and decompression can be done.
- A. Decompression can be done on the database servers.
- B. Compression can be done on the Exadata storage servers.
- C. Compression can be done on the database servers.
- D. Decompression can be done on the Exadata storage servers.
Answer : A,C,D
Explanation:
* decompression
/ Queries run directly on Hybrid Columnar Compressed data does not require the data to be decompressed
/ Data that is required to satisfy a query predicate does not need to be decompressed; only the columns and rows being returned to the client are decompressed in memory
/ The decompression process typically takes place on the Oracle
Exadata Storage Server in order to maximize performance and
offload processing from the database server.
Which two are true concerning the allocation of I/O resources by the IORM within the
CELLSRV process?
- A. Control File I/O is managed automatically at high priority by IORM.
- B. Control File I/O is considered part of the SYSTEM resource Consume group by IORM.
- C. Log Writer I/O to the Smart Flash Log is considered part of the SYSTEM resource consumer group by IORM.
- D. Log Writer I/O to the Smart Flash Log is managed automatically at high priority by IORM.
- E. Database Writer I/O is managed automatically at normal priority by IORM.
- F. Database Writer I/O is considered part of the SYSTEM resource consumer group by IORM.
Answer : A,E
Explanation: Note:
* IORM Rules
IORM is only "engaged" when needed.
/ (A) Redo and control file writes always take precedence.
/ (E) DBWR (database writer) writes are scheduled at the same priority as user IO.
/ IORM does not intervene if there is only one active consumer group on one database.
/ Any disk allocation that is not fully utilized is made available to other workloads in relation to the configured resource plans.
/ Background IO is scheduled based on their priority relative to user IO.
/ For each cell disk, each database accessing the cell has one IO queue per consumer group and three background queues.
/ Background IO queues are mapped to "high", "medium", and "low" priority requests with different IO types mapped to each queue.
/ If no intradatabase plan is set, all non-background IO requests are grouped into a single consumer group called OTHER_GROUPS.
Reference: Using IORM with Exadata
Which three are true abort Enterprise Manager plug- in configuration for the Database
Machine?
- A. There are several separate plug-ins for Grid Control.
- B. There is one plug-in for Cloud Control.
- C. There are several separate plug-ins for Cloud Control.
- D. Some plug-ins require SNMP trap forwarders.
- E. All plug-ins require SNMP trap forwarders.
- F. There is one plug-in for Grid Control.
Answer : A,C,D
What is the benefit of bonding the client access network configuration?
- A. Improved performance
- B. Improved reliability
- C. Both improved performance and reliability
- D. A Single Client Access Name (SCAN)
- E. Improved monitoring
Answer : B
Reference: Oracle Exadata Database Machine - Backup & Recovery Sizing: Tape Backups
Which three are true regarding the use of Storage Indexes?
- A. Different storage regions may have different columns indexed for the same table.
- B. A Storage index is automatically maintained by CELLSRV based on the filter columns of the offload SQL.
- C. The use of Storage indexes for a particular database can be disabled by using an I/O Resource Manager Database Plan.
- D. Storage Indexes occupy space in the Smart Flash Cache.
- E. The use of Storage Indexes for particular categories of I/O can be disabled by using an I/O Resource Manager Category Plan.
- F. A maximum of eight table columns for any table are Indexed per storage region.
Answer : A,B,F
Explanation:
Note:
. All the limitations to smart scans apply to
storage indexes. They do not work with joins. Bind variables are supported, however its slightly more restrictive than regular indexes/queries.
* The storage index is stored in the memory on each of the Exadata storage cells and is created and maintained transparently. However, if a storage cell is shutdown or rebooted the storage index will be lost from memory and will be recreated on subsequent accesses to the data after the cell has been brought back online.
* Storage Indexes are a very powerful capability provided in Exadata storage that helps avoid I/O operations. The Exadata Storage Server Software creates and maintains a
Storage Index (that is, metadata about the database objects) in the Exadata cell. The
Storage Index keeps track of minimum and maximum values of columns for tables stored on that cell. When a query specifies a WHERE clause, but before any I/O is done, the
Exadata software examines the Storage Index to determine if rows with the specified column value exist in the cell by comparing the column value to the minimum and maximum values maintained in the Storage Index. If the column value is outside the minimum and maximum range, scan I/O for that query is avoided. Many SQL Operations run dramatically faster because large numbers of I/O operations are automatically replaced by a few lookups. To minimize operational overhead, Storage Indexes are created and maintained transparently and automatically by the Exadata Storage Server Software.
A read-only application is in development and is using a test database on a Database
Machine. You are examining SQL statements from this application in an attempt to determine which ones will benefit from the Exadata Smart scan capability.
The following is true about the tables used by the application:
1. The data for the tables has just been loaded.
2. There are no applications accessing the tables currently.
3. None of the indexes are compressed or reverse key indexes.
4. The tables use the default organization type data.
5. The only data types for the table are varchar (2), number, or date.
6. The largest number of columns for any table is 29.
7. No access is based on ROWID, or virtual columns.
Which two access paths will always generate either a set of cell smart table scan or a set of cell smart index scan requested?
- A. Full scans on sorted hash clustered tables executed in parallel
- B. Full table scans on index organized tables executed in parallel.
- C. Full table scans on heap tables executed in parallel
- D. Full scans on index clustered tables executed in parallel
- E. full scans on hash clustered tables executed in serially
- F. fast full scans on B*Tree indexes executed in parallel
- G. full index scans on B*Tree indexes executed in parallel
Answer : C,F
Identify the correct sequence of commands to completely power off a Database Machine in an Orderly fashion:
1. Execute crsctl stop cluster all as the grid user from one database server.
2. Execute crsctl stop cluster all as the root user from one database server.
3. Power off all network switches using their power switch.
4. Execute crsctl stop cluster all as the root user from one database server.
5. Execute crsctl stop cluster all as the grid user from one database server.
6. Power off the rack using the power switches on the PDUs.
7. Execute shutdown h now on all database servers.
8. Execute shutdown h now on all Exadata storage servers.
9. Execute shutdown h now on all servers.
- A. 1, 9, 3 and 6
- B. 2, 9 and 6
- C. 4, 7, 8, 3 and 6
- D. 5, 8, 7, 3 and 6
- E. 2, 8, 7, 3 and 6
- F. 1, 8, 7, 3 and 6
- G. 2, 7, 8 and 6
- H. 2, 8, 7 and 6
Answer : G
You configuring has two half racks, one with high capacity disks and other with high performance disks and high capacity expansion half rack.
There are two RAC clusters, one on each half rack, which have separate storage grids, each consisting of some of the storage servers in the configuration.
You are planning your deployment of Enterprise Manager to monitor all the components of this multi-rack Database Machine, and must provide for high availability of the monitoring infrastructure.
If the host running the agent which has database machine targets bound to it fails, the monitoring of these targets must be another agent.
Which two are true regarding the configuration used to support this?
- A. Enterprise manager support must be deployed to only one Enterprise Manager Agent in each cluster.
- B. A secondary agent must be deployed on a database server in the same cluster as the server hosting the primary agent.
- C. Enterprise Manager support must be deployed to all Enterprise Manager Agents in each cluster.
- D. A secondary agent may be deployed on a database server in a different cluster than the server hosting the primary agent.
- E. A secondary agent must be deployed on a database server in a different cluster than the server hosting the primary agent.
- F. Enterprise Manager support must be deployed to at least two Enterprise Manager Agents in each of the two RAC clusters.
Answer : A,D
Explanation:
Note:
* Instructions for configuring a high availability solution for the Exadata Storage cell or any other Exadata plug-in are documented in the Oracle Database Machine Monitoring Best
Practices (Doc ID 1110675.1) document located in My Oracle Support
* High Availability for Plug-Ins
Normally a plug-in target is bound to a specific agent
If the agent is down the target cannot be monitored
A procedure exists to facilitate target failover to a secondary agent
* The Enterprise Manager agent must be deployed to all compute nodes of the Exadata
Database Machine.
* The Oracle ILOM plug-in monitors the Oracle ILOM service processor in a compute node for hardware events and records sensor data to the Oracle
Enterprise Manager Repository.
The ILOM plug-in is deployed to the Enterprise Manager (EM) Agent on the first compute node in an Oracle Database Machine, and only that EM agent communicates with the EM Management Server and Repository for all ILOM database server service processors in the Oracle Database Machine.
* OEM Agent and Exadata Plug-ins
1. OEM Agent and Plug-Ins
are deployed under Oracle
Home -
2. Agent incorporates
additional functionality in
Plug-In -
3. Agent and Plug-in
DB Server on Exadata DBM -
3. Agent and Plug-in
communicates with
Storage Server -
4. Plug-Ins are available for
monitoring all Exadata
hardware components
5. OEM Agent communicates
with the OEM
You must drop all celldisks on all the cells in a quarter rack as part of a reconfiguration project, to support normal redundancy interleaving.
Select two actions that describe the operating system (O/S) account on the cells to which you should log in, and the tool that may be used to drop the celldisks.
- A. To the CELLMONITOR account using CELLCLI interactively on each cell.
- B. To CELLADMIN account calling CELLCLI on all cells using DCLI
- C. To either the CELIMONITOR or the CELLADMIN account calling CELLCLI on all cells using DCLI
- D. To the CELLMONITOR account calling CELLCLI on all cells using DCLI
- E. To the CELLADMIN account using CELLCLI interactively on each cell
- F. To either the CELLMONITOR or CELLADMIN account calling interactively on each cell
Answer : B,E
Explanation:
Note:
* Each Exadata Storage cell can be monitored, configured, and maintained using the cellcli command line interface. To invoke the CLI, simply login to the Exadata cell as cellmonitor, celladmin, or root, and type "cellcli". Within cellcli, a wide range of commands can be invoked to monitor the cell.
* While connected to cellcli as the Linux account celladmin, you can perform all cellcli commands except calibrate.
While logged into the cell server as cellmonitor, you can do any "read-only" commands; you cannot change any configuration or attributes.
Which statement is true about operating systems on database Machine multi-rack configuration consisting of two full racks and one Exadata storage rack?
- A. All Exadata storage servers and all database servers must run the Oracle Linux O/S and X3-8 database server may run the Oracle Solaris O/S.
- B. All Exadata storage servers must run the Oracle Linux O/S and all database servers within the same cluster must run the Oracle Linux O/s.
- C. All Exadata storage servers must run the Oracle Linux O/S and all database servers within the same cluster must run the same O/s.
- D. All Exadata Storage Servers must run the Oracle Solaris O/S and all database servers within the same cluster must run the same O/S.
- E. All Exadata storage servers in the same cluster must run the same O/S but Exadata Storage Servers in different clusters may run a different O/S.
Answer : C
You are monitoring and evaluating a create index statement on your Database Machine and have run the following query after executing statement, providing the output. Shown:
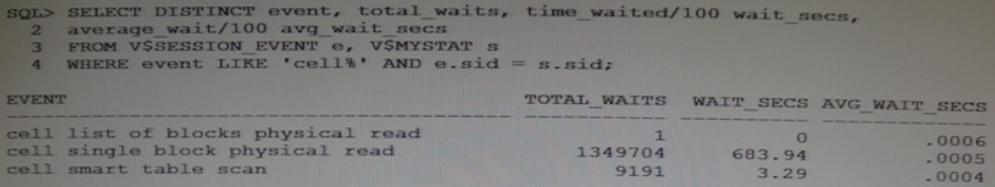
Select two reasons why the statement would have produced so many cell single block physical read waits compared to cell smart table scan waits.
- A. There are huge numbers of migrated rows in the table on which the index is being built.
- B. There is an uncommitted transaction that has modified one block of the table on which the index is being built, in each cell.
- C. There is a transaction that has modified one block of the table on which the index is being built in each cell, which committed after the create index began.
- D. There are huge numbers of chained rows in the table on which the index is being built.
- E. There is a ROWID column in the table on which the index is being built.
Answer : A,D
Explanation: A: It could be that row migration.
D: It could be that row migration or chained rows could cause it.
Note:
* Some facts about scans:
Scans exists in OLTP systems -
Exadata smart scan requires a direct path read.
A direct path read is chosen at runtime based on internal heuristics
The STORAGE clause in an explain plan doesnt necessarily mean you will perform a smart scan.
* The buffer caching in certain OLTP environments can
occasionally induce conventional reads when smart
scan is faster.
* Typically see cell multiblock physical read instead of cell smart table scan waits
* No one-size-fits-all solution can be given here but it is
very fixable.
Which two activities are supported on the storage servers in the Database Machine?
- A. Installing an alternative package manager
- B. configuring secure shell user equivalency for the callmonitor user
- C. changing root password
- D. upgrading the Storage Server software package using RPN
- E. upgrading a device driver for hard disks when inserting a replacement disk after a hard disk failure
Answer : B,C
You are examining the existing IORM configuration on the cells of Database Machine, to see if they require my modifications based on recent changes to various workloads.
All seven cells in your X3-2 half-rack shown the following:
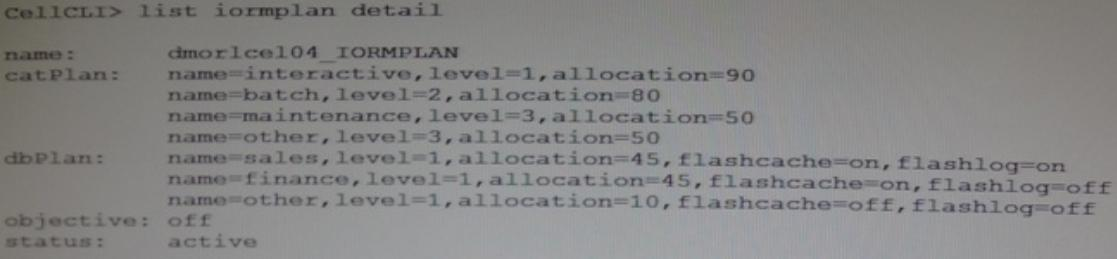
Which two are true about I/O to the cells using this plan?
- A. I/O requests in the batch category may use flashcache if the I/O is from the sales finance database, and these I/O requests are guaranteed to get 80% of the I/O if the interactive category I/Os use no more than 20%.
- B. I/O requests made by sessions in the marketing database may use flashing and flashcache if no other categories or database or database are using flashing and flashcache at the same time.
- C. I/O requested in the interactive category may use flashdns if the I/O is from the sales or finance databases, and these I/O requests are guaranteed to get 90% of the I/O if the enough I/Os are issued in this category.
- D. I/O requests from the sales database may use flashing regardless of the I/O category.
- E. No I/Os in any category or from any database may use flashing or flashcache because the objective is off.
Answer : A,D
Which three statements are true regarding the configuration of Auto Service Request
(ASR) on your Database Machine?
- A. HTTPS connectivity must be enabled from the ASK Manager host to the internet.
- B. ASR Manager must be installed on one of the database servers.
- C. Oracle Solaris must be used on the server where ASK Manager is installed.
- D. SMTP must be enabled on at least one database server.
- E. Oracle Linux must be used on the server where ASR Manager is installed
- F. ASR Manager may be installed on any type of server running Oracle Linux.
- G. ASR Manager may be installed on any type of server running Oracle Solaris.
Answer : A,F,G
Explanation: A: Before installing ASR, please ensure the following conditions are met:
/ (A) Ensure connectivity to the Internet using HTTPS.
/ Make sure you have access to My Oracle Support and that your contact information is correct and current.
/ Make sure all of your assets have a Contact assigned and that the contact is correct and current.
/ Identify and designate a system to serve as ASR Manager.
/ Identify and verify ASR assets.
F, G (not C, not E, not B): The recommended configuration is to install the ASR Manager, which receives fault telemetry information from the servers in Oracle Exadata Database
Machine, on an external standalone server. This server must run Solaris or Linux as the operating system.
Reference: Oracle Auto Service Request Exadata Database Machine Quick Installation
Guide -

